Departments
In the PT department, we provide exercise therapy and physical therapy to patients based on doctor's instructions, with the aim of restoring the basic functions and mobility of the body that have been lost. We also work with other medical staff to provide appropriate interventions to help patients return to society and prevent the recurrence or worsening of illness. In our department, the PT department is made up of the following three teams (Central Team, Internal Disorder Team, and Orthopedic Team), and we have established a system to provide specialized treatment tailored to each patient's condition.
I am mainly responsible for patients in the neurosurgery ward, neurology ward, and SCU.
We treat conditions such as cerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, brain tumors, hydrocephalus, trigeminal nerve palsy, facial nerve palsy, and spinal and spinal cord diseases.
It covers cerebral infarction, Parkinson's disease, progressive supranuclear palsy, multiple system atrophy, multiple sclerosis, spinocerebellar degeneration, Guillain-Barré syndrome, ALS, myasthenia gravis, and peripheral neuropathy.
The team meets weekly for conferences to discuss the appropriateness and direction of these treatments. We also participate in ward conferences as described below.

We hold a conference once a week with a range of professionals, including nurses, medical social workers, physical therapists, occupational therapists, and speech-language-hearing therapists, to ensure that hospitalized patients can be discharged or transferred to their homes or rehabilitation hospitals or facilities without anxiety.
We share information about patients' conditions in the ward, their recovery through rehabilitation, and their social backgrounds with a multidisciplinary team, and provide support such as coordinating social resources to ensure that patients and their families can live safely after discharge in accordance with their wishes.
On weekends, the frequency of rehabilitation interventions decreases, and patients' activity levels also decline. Patients who require intervention are selected, and the ward nurses, physiotherapists, occupational therapists, and speech-language-hearing therapists in charge meet to share the rehabilitation menu needed for the weekend and discuss how to carry out weekend rehabilitation safely. Ward staff and rehabilitation staff also consider assistance methods and room environment settings that are suitable for each individual patient.
Starting in 2019, a full-time physical therapist was assigned to SCU.
Our hospital has a nine-bed Stroke Care Unit (SCU), an intensive care unit specializing in cerebrovascular disease. A dedicated SCU physiotherapist is always present in the SCU, sharing information with doctors and nurses and providing rehabilitation tailored to the patient's changing condition. Patients' rehabilitation progress is also shared, and with the cooperation of nurses, rehabilitation that can be done in the ward is carried out on weekends (weekend rehabilitation).

Weekend rehabilitation pamphlet

Upper limb rehabilitation items

The course focused on lectures on physical therapy evaluation of central nervous system diseases, how to interpret brain images, risk management in the acute phase of cerebrovascular disease, brain surgery and postoperative management, pathology of stroke and brain tumor, Parkinson's disease, ataxia, orthotic therapy, electrical stimulation therapy, and posture control.In addition, case conferences and supervision were held, and clinical questions were shared and addressed within the team.
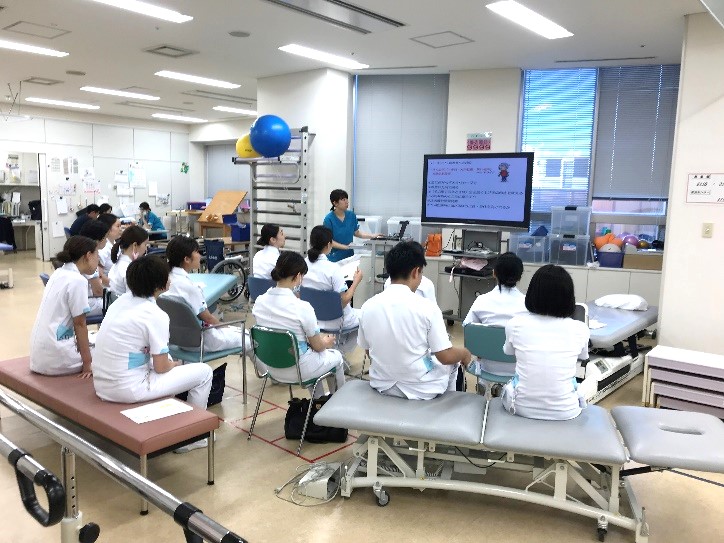

Together with staff from the neurosurgery ward and neurology ward, we shared knowledge and points to note about the characteristics of movements in each disease and how to assist patients, and practiced actual methods together.
We are creating a database for patients admitted to the SCU and those hospitalized for Parkinson's disease and Parkinson's syndrome. We are also working hard every day to be able to submit case reports and present at academic conferences on the progress and effectiveness of treatment.
The Internal Disability Team provides rehabilitation to patients with a wide range of illnesses, including respiratory, circulatory, digestive, blood, and metabolic disorders, from an early stage after admission.
By having physical therapists involved from early on after admission, including in intensive care areas (ICU, HCU, etc.), we aim to prevent a decline in physical and mental function during hospitalization and improve daily living functions for early discharge. For patients scheduled for thoracotomy or abdominal surgery, we provide thorough preoperative instruction to prevent postoperative complications, and begin rehabilitation early after surgery to ensure a smooth discharge. We also actively hold conferences in each ward, fostering cooperation between various professions, including doctors, nurses, pharmacists, registered dietitians, and social workers. In the renal failure and heart failure classes, we also work with other professionals to provide disease management guidance to patients.
In 2019, we launched the Kitano Flying Disc Club in collaboration with the Department of Respiratory Medicine, targeting patients with chronic respiratory diseases. We also provide rehabilitation for patients with chronic respiratory diseases through educational hospitalization. We also provide "cancer rehabilitation" for patients with lung cancer, leukemia, digestive cancer, and other conditions, and currently receive over 50 requests per month. In our renal failure and heart failure classes, we collaborate with other professionals to provide disease management guidance to patients. We also actively participate in various training sessions and present at academic conferences, striving to provide treatment based on the latest knowledge and scientific evidence.
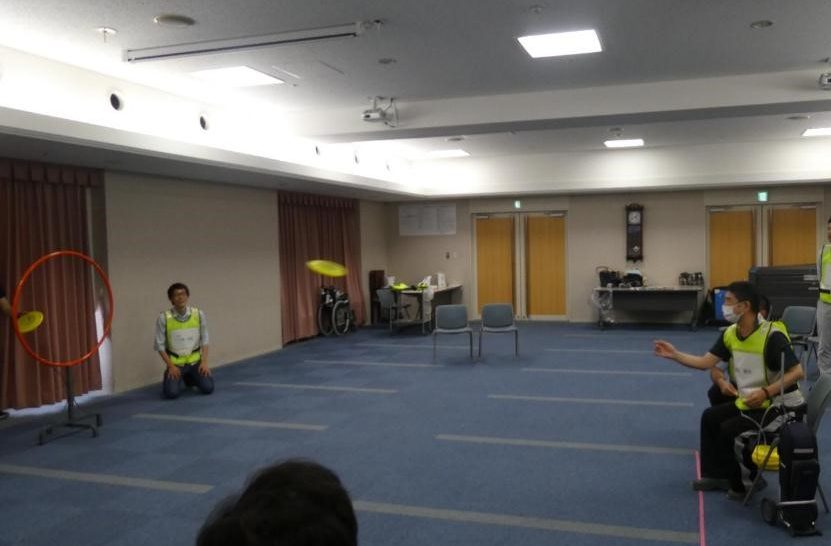

As part of our hospital's respiratory medicine efforts, doctors, nurses, physical therapists, pharmacists, and nutritionists work together to hold flying disc competitions for patients with chronic respiratory failure, with the aim of increasing activity levels and promoting social participation in those with chronic respiratory failure. Flying disc is a low-intensity exercise that can be done indoors or outdoors, making it a sport that can be played all year round. Before the competition, participants undergo health checks such as blood pressure measurements, warm-up exercises, and respiratory status checks, so you can participate with peace of mind.
Doctors, nurses, nutritionists and other professionals give lectures to people with chronic kidney disease and their families, and physiotherapists are involved twice a year in providing demonstrations and focusing on safe exercises to deepen understanding. Physiotherapists are also involved in Kitano Kidney Day, which is held once a year and includes lectures and hands-on experiences on kidney disease.
In our heart failure classes, we lecture patients and their families on exercise therapy. Exercise therapy is used in conjunction with dietary therapy and drug therapy and is treated as part of heart failure treatment. Treatment does not end once heart failure has improved; subsequent improvements in physical strength and disease management are important, which also helps prevent re-hospitalization. As physical therapists, we explain the type, frequency, and intensity of exercise tailored to each patient's needs during and after hospitalization.
Our main treatments are spinal diseases (cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine), joint surgery (total knee replacement, total hip replacement), various trauma (fractures of the spine, upper limbs, and lower limbs, etc.), metastatic bone tumors, and various collagen diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, dermatomyositis, etc.).
Our orthopedic team consists of six physical therapists (one of whom also works as a visiting therapist) and one masseuse. To prevent decline in physical function and facilitate early discharge, we provide exercise therapy, relaxation techniques, various manual therapies, physical therapy such as electrical stimulation and heat therapy, and daily living activity training from early after admission or surgery. To appropriately respond to various illnesses, we also educate young staff, provide necessary training equipment, and establish training standards and procedures for clinical pathways and standard programs for each illness. For educational hospitalizations of rheumatoid arthritis patients, we collaborate with other professionals to provide rehabilitation and disease management during hospitalization.



Based on doctor's instructions, we provide treatment using occupational activities for patients who are experiencing or are expected to experience difficulties in daily life, in order to help them regain an independent lifestyle. Specifically, we train the motor functions of the upper limbs and fingers, as well as higher brain functions. We also provide repeated practice for the movement tasks that are actually difficult for the patient, and propose and create assistive devices and prosthetics as needed.

The aim is to restore higher brain functions and eating and swallowing abilities in order to acquire communication skills and the ability to eat safely.

This test simultaneously measures cardiac function, pulmonary function, and skeletal muscle function during exercise. It is performed by a therapist in the presence of the patient's doctor. The anaerobic threshold (AT), an index of exercise capacity and myocardial function, is calculated using an exhaled gas analyzer and is used as an index of exercise load during rehabilitation and to assess its effectiveness.
SOLIUS is a low-frequency therapy device that aims to maintain skeletal muscle function through electrical stimulation for early rehabilitation after surgery. Muscle weakness after surgery has been reported to be caused not only by bed rest and inactivity, but also by the invasiveness of surgery. From perioperative rehabilitation to exercise after discharge, SOLIUS can be used with minimal physical strain, and is expected to help maintain muscle strength and prevent functional decline.

By quantitatively analyzing the basic components that make up the body - body water, protein, minerals, and body fat - it is possible to measure muscle mass, nutritional status, whether the body is swollen, etc. At our hospital, we use it to measure changes in muscle mass before and after surgery, evaluate physical function in various fields (cardiology and neurology), analyze sarcopenia, etc.