Departments
| attending physician | Dr. Kosuke Takeda and Dr. Namiko Ishikawa |
|---|---|
| Outpatient | Hemangioma Outpatient Clinic (Friday) |
Vascular lesions on the surface and soft tissues of the body have traditionally been called hemangiomas, but in 1996, the International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies (ISSVA) classification broadly divided vascular lesions into hemangiomas and vascular malformations.
Hemangiomas have previously been called strawberry hemangiomas or simple hemangiomas, but in recent years they have been classified as infantile hemangiomas and capillary malformations, respectively.
Vascular malformations are classified into capillary malformations (formerly known as simple hemangiomas), venous malformations, and arteriovenous malformations, but there may also be a mixture of these lesions.
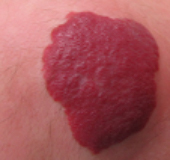
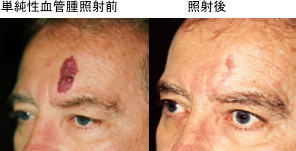
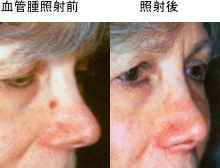
Hemangiomas often develop in newborn babies, but they can also be present at birth.
By about the age of one year, the hemangiomas will gradually swell and take on a strawberry-like shape, but will naturally shrink and often regress by the time the child reaches the early grades of elementary school. However, if the hemangiomas are large, they may develop ulcers and bleed, and once the hemangiomas have subsided, wrinkled scars or red or brown discoloration of the skin may remain. In order to prevent these aftereffects, oral medication and laser treatments have recently become more common before the hemangiomas become too large.
In addition, if it occurs on the eyelids, buttocks, around the mouth, or inside the mouth, it can cause vision problems, infection, eating disorders, and airway compression, so oral treatment will be administered early on, and we recommend that you see a specialist.
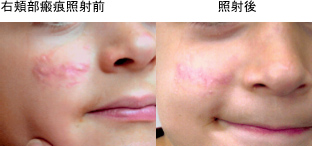
Laser treatment utilizes the absorption of red-sensitive laser light by the lesion. Our department uses a 595nm tunable dye laser, the V-Beam, which allows for adjustable laser pulse width (irradiation time). Because it is selectively absorbed by hemoglobin in the blood, the hemoglobin absorbs the laser energy and converts it into heat, destroying the inner walls of the blood vessels and occluding them, eliminating the red color. Equipped with a dynamic cooling device, the laser can irradiate vascular lesions while protecting the skin by spraying ice just before laser irradiation, reducing the risk of burns. Vascular lesions are covered by insurance (see the Cosmetic section). Because results vary from person to person, multiple treatments may be required.
"V-Beam" is a pulsed dye laser that is an improved version of the "dye laser" developed for the treatment of vascular lesions. Because the pulse width is variable, it can be used for a variety of purposes, including not only treating red birthmarks, but also redness of the face, acne, acne scars, and rosacea.
The 595-nanometer laser light emitted from Vbeam is selectively absorbed by hemoglobin in the blood and converted into heat, resulting in a therapeutic effect. Furthermore, Vbeam's adjustable laser pulse width (irradiation time) makes it possible to appropriately set the irradiation time according to the diameter of the capillaries. The device is equipped with a skin cooling device, which minimizes damage to the epidermis and reduces pain during irradiation.
Candela's Vbeam has been approved for use in Japan by the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, and is therefore covered by health insurance for the treatment of vascular lesions such as port wine stains and hemangiomas. Furthermore, although not covered by health insurance, Vbeam irradiation stimulates collagen production, making it possible to treat skin rejuvenation, age spots, fine wrinkles, and other conditions.
It is effective for redness such as simple hemangioma, strawberry hematoma, telangiectasia, and rosacea. It is also effective for areas that are red due to inflammation such as acne. It is also effective for fine wrinkles.
In cases of red bruises or capillary dilation, the blood in the blood vessels is burned, causing previously red areas to turn black or purple (internal bleeding), but this will be gradually absorbed over 2-3 weeks. There are almost no side effects after treatment for acne inflammation or fine wrinkle removal. Treatment results vary from person to person, so several treatments may be required.