
Departments
The goal of treating facial bone fractures is to restore function and form. Typical symptoms of functional impairment include double vision, trismus, and malocclusion. Morphological abnormalities are not necessarily indications for surgical treatment, and surgical treatment is considered if the patient is concerned about the morphological abnormality. Here we will provide an overview of symptoms and treatment for each of the most common fractures.
Generally, surgery involves fixing the fracture using the patient's own bone (ilium or bone from the anterior wall of the maxilla), a thin titanium plate, or an absorbable osteotomical plate.
In our department, we use endoscopes to perform surgery with fewer and smaller incisions. Depending on the location of the fracture, emergency surgery may be necessary, so we recommend that you visit a plastic surgeon as soon as possible after the injury.
Fractures can cause morphological abnormalities such as a saddle nose or a crooked nose, which can lead to nasal stenosis. Treatment is usually initiated after the swelling has subsided and the deformity has become clear. Treatment involves using nasal bone reduction forceps to set the bent bone back into place from within the nasal cavity. Treatment is usually performed under local anesthesia, but if time has passed since the injury and reduction is difficult, or in the case of children, it may be performed under general anesthesia.
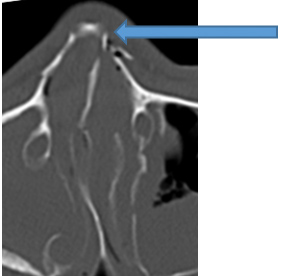
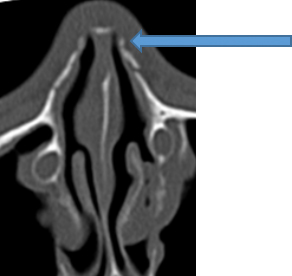
The inner and outer walls of the orbital wall, located deep inside the orbit (the space that holds the eyeball), are made of thin bone. Therefore, when strong pressure is applied around the eye, the thin bones of the inner orbital wall and orbital floor can fracture, causing a blowout fracture into the adjacent sinus. This type of fracture is also known as an "orbital blowout fracture." If the fat tissue or eye muscles inside the orbit protrude beyond the fracture site, the eye may become sunken (enophthalmos), eye movement may become impaired, resulting in double vision (diplopia), and nausea. Sensory nerves run through the orbital floor, and if damaged, the sensation from the cheek to the upper lip may become numb. Blowing your nose also produces a blood-tinged mucus. Blowing your nose in this condition can actually cause air to enter the tissues around the eye through the fracture, leading to vision impairment in severe cases. Therefore, do not blow your nose. If you experience symptoms such as double vision, we recommend consulting a specialist, such as a plastic surgeon or ophthalmologist. This is one of the fractures where determining whether or not surgery is appropriate is difficult.
In our department, we perform endoscopic correction of displaced bones and then fix the corrected bones using metal (titanium) plates or the patient's own bone.
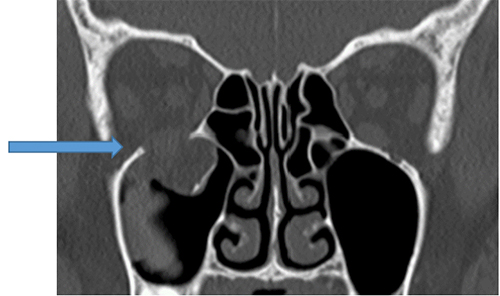
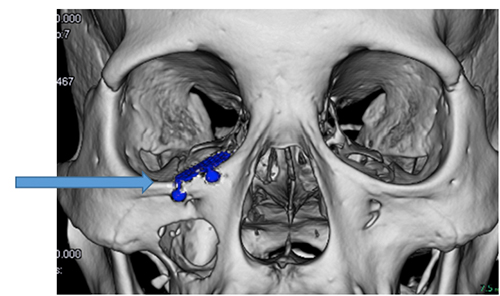
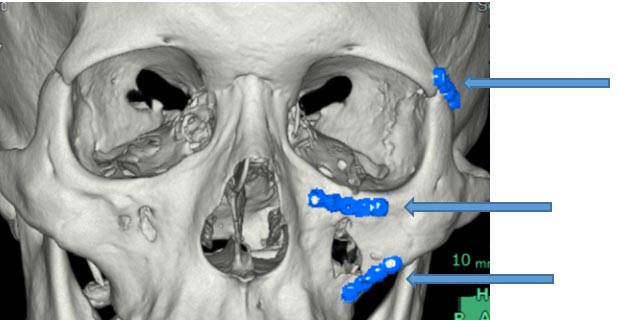
This is the area that often fractures when the cheekbone is hit. Symptoms include numbness or flattening of the cheek on the injured side, misalignment of the teeth (malocclusion), difficulty opening the mouth, and double vision (diplopia). Because the cheekbone is connected to the frontal bone, temporal bone, and maxilla at three points, fractures at these three points, known as a "tripod fracture," often occur. The surgical procedure varies greatly depending on the severity and symptoms of the fracture, but it involves reducing the displacement of the cheekbone and then fixing the reduced bone with a metal (titanium) plate, absorbable plate, or the patient's own bone.

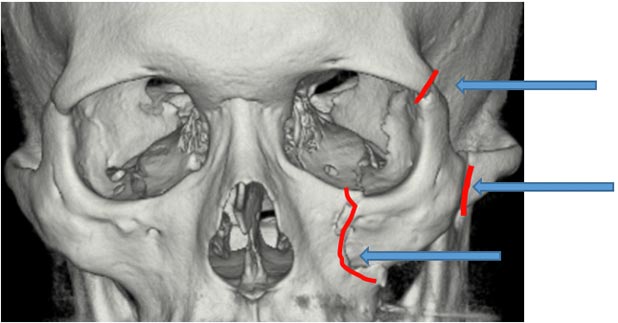
Preoperative CT
Injuries often occur due to a blow to the jaw, and after the injury, patients become aware of abnormalities in the alignment of their teeth. The main goal of treatment is to restore the bite, which is repaired through surgery, and a procedure called intermaxillary fixation, in which the upper and lower jaws are fixed with wires and rubber bands, is performed for several weeks. The bones that have shifted due to the fracture are returned to their original position and fixed with a plate.