
Departments
The heart acts as a pump to send blood to the entire body. The blood vessels that send blood to the heart are called coronary arteries, but if the coronary arteries become narrowed or blocked due to arteriosclerosis or other reasons, nutrients and oxygen will not reach the heart sufficiently. This condition is called ischemia, and can cause angina pectoris and myocardial infarction.
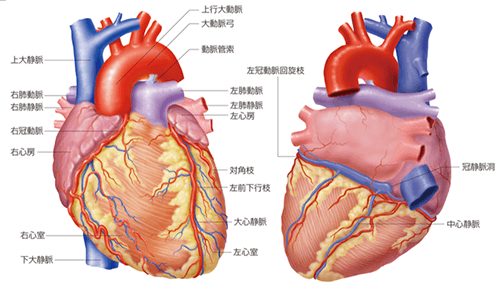
When the coronary arteries narrow and become ischemic, an angina attack occurs.During an attack, symptoms such as tightness in the neck, back, left arm, upper abdomen, etc., as well as stomach discomfort and difficulty breathing may appear, not just in the anterior chest. Cold sweats, nausea, and vomiting may also occur.there is.
Myocardial ischemia can occur even without symptoms, and is more common in people with diabetes and the elderly.
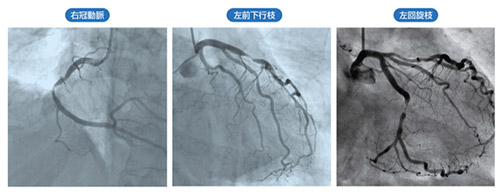
If ischemic heart disease is suspected based on a medical interview or electrocardiogram, we will perform echocardiography, exercise electrocardiogram, Holter electrocardiogram, cardiac CT, myocardial scintigraphy, cardiac catheterization, etc. In elective cases, we will quickly diagnose using cardiac CT, myocardial scintigraphy, etc., and then perform catheterization. When it is necessary to accurately determine whether or not coronary artery stenosis should be treated, we measure FFR (fractional flow reserve).
Treatment options include:Drug treatment,catheter treatment,surgeryThere is.
The catheter treatment method, which widens narrowed blood vessels using a catheter and resumes blood flow, is called "balloon therapy."Balloon therapy" and implanting a mesh metal tube (stent) "Stent treatmentDuring catheter treatment, intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) and optical coherence tomography (OCT) are used to analyze the lesion in detail before treatment is performed.
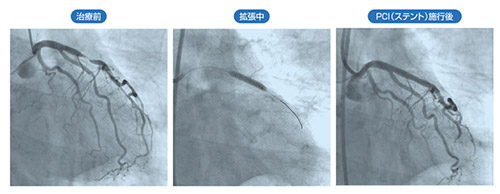

Catheter treatments have a certain frequency of restenosis (re-narrowing of the blood vessels). In the days of balloon treatment, restenosis was observed at 30-40%, but with the use of stents (BMS), this rate has dropped to around 20%, and with drug-eluting stents (DES), it has dropped to 10% or less.
Drug-eluting balloons (DCBs) are sometimes used for restenotic lesions and small blood vessels. The drug (paclitaxel) coated on the surface of the balloon comes into contact with the blood vessel wall when the balloon is expanded, and migrates to the blood vessel wall, thereby exerting an inhibitory effect on restenosis.
A diamond-tipped burr rotates at high speed to remove hardened arteriosclerotic lesions caused by calcification.When arteriosclerosis becomes calcified and hardens, expansion with a normal balloon becomes poor, and even if a stent is placed in a state where expansion is poor, the stent itself will not expand sufficiently, increasing the possibility of restenosis.
The causeLifestyle-related diseases such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, and diabetesCatheter therapy and bypass surgery do not completely cure arteriosclerosis. It is important to prevent the progression of arteriosclerosis.We also provide lifestyle guidance to prevent recurrence through smoking cessation, dietary therapy, exercise therapy, etc..