Departments
Acute scrotum is characterized by sudden pain, redness, and swelling of the scrotum, and requires immediate diagnosis and treatment. Causes of acute scrotum include testicular torsion and epididymitis.
Among them, the most important one isTesticular torsionis.
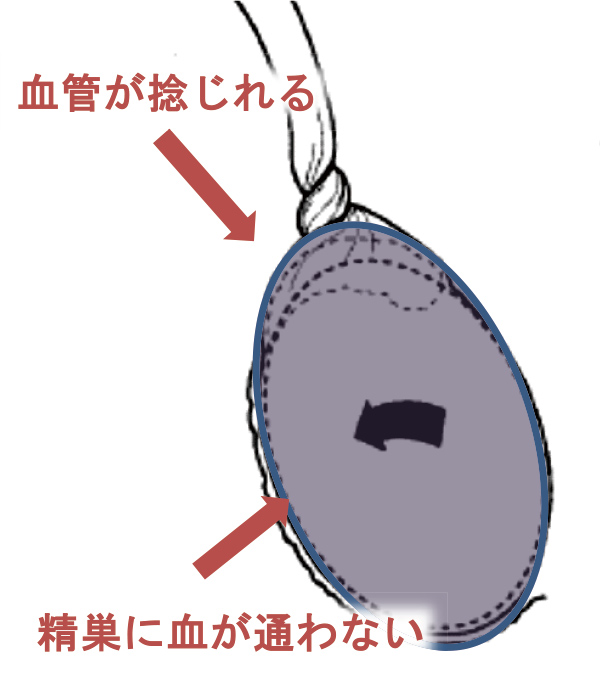
This is a condition in which the testicle suddenly twists, causing the blood vessels leading to the testicle to twist as well, cutting off blood flow to the testicle. If this condition is left untreated, the testicle will necrose (rot). This condition requires immediate surgery.
Symptoms include sudden pain, swelling, redness of the scrotum, abdominal pain, and vomiting.

This is done through physical examination and ultrasound. Ultrasound is used to check the blood flow to the testicles. However, ultrasound may not be able to provide an accurate diagnosis. In such cases, direct confirmation is required through surgery.
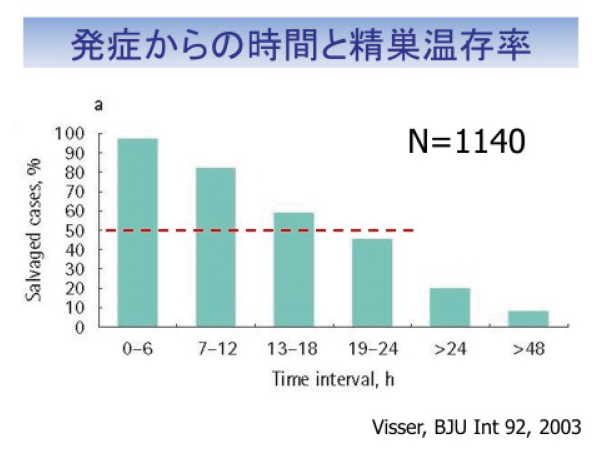
Emergency surgery is required. The surgery involves cutting open the scrotum and untwisting the testicle. The condition of the testicle (whether it can be preserved) is observed. If it looks like it can be preserved, the testicle is fixed to the scrotum. If it is completely necrotic, unfortunately, the testicle will have to be removed. The earlier the condition is treated after the onset of the disease, the higher the chances of preserving the testicle.
Furthermore, in most cases where testicular torsion occurs, the opposite testicle is also prone to torsion. As there is a possibility that the opposite testicle may also torsion in the future, testicular fixation on the opposite side is also performed at the same time.
Surgery may diagnose that testicular torsion is not the cause. However, if testicular torsion is present, the chances of preserving the testicle decrease over time, so surgery is recommended if testicular torsion is suspected.
After surgery, the condition of the testicles will be monitored in the outpatient clinic. Even if it is determined that the testicles can be preserved at the time of surgery, there are some patients who have experienced significant damage to the testicles, resulting in gradual atrophy of the testicles after surgery.