Home > Departments > Pediatric Surgery > Target diseases > Ovarian cysts in newborns

Departments
Medical Departments
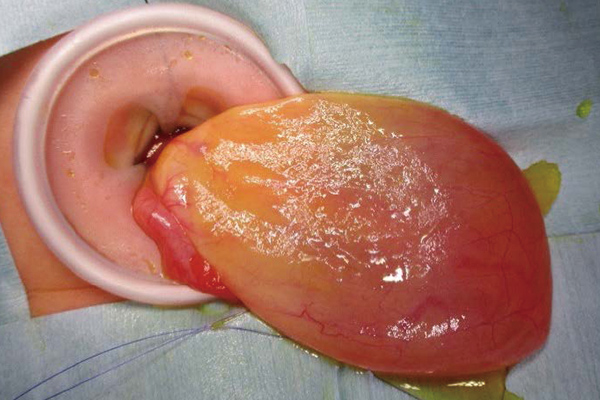
During fetal development, the ovaries sometimes become enlarged due to fluid accumulation caused by the influence of the mother's hormones. However, in many cases, after birth, the influence of the mother's female hormones disappears and the ovaries can be expected to shrink naturally. However, if the ovaries grow larger than 4-5cm, there is a risk that they may twist and rot. For this reason, in the case of large ovarian cysts, surgery may be performed to open the ovarian sac and drain the fluid inside.
Generally, it is discovered during fetal development through ultrasound. After birth, the size of the ovaries is measured through ultrasound and the need for treatment is determined. Ovaries may already be twisted during fetal development.
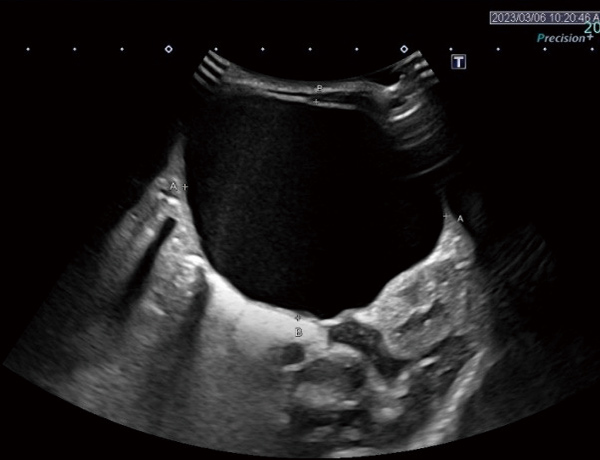
Non-torsion ovarian cysts are often clean inside.
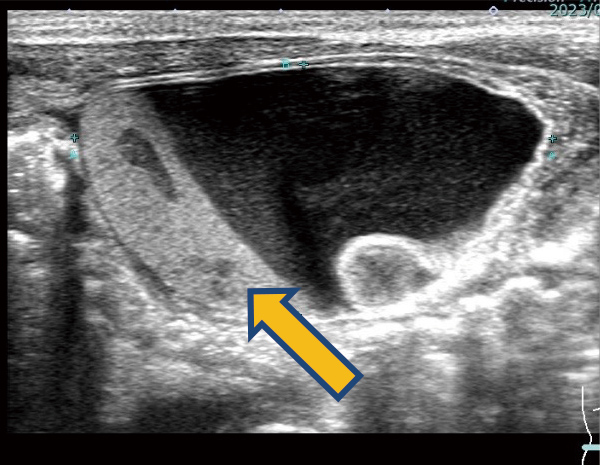
Torsed ovarian cysts often have lumpy internal structures due to bleeding, etc.
In most cases, surgery can be performed through a small incision in the belly button. The scar is not very noticeable. Once the water has been drained through surgery, it rarely accumulates again.