Departments
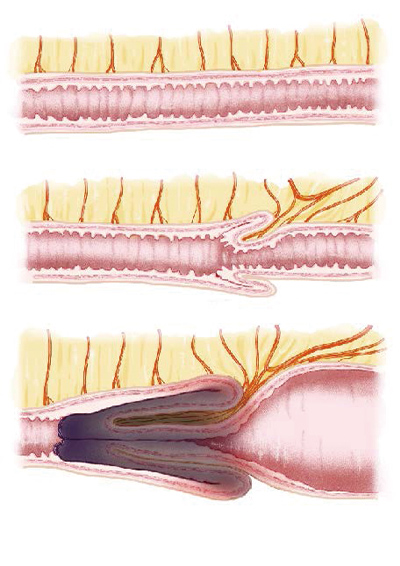
Intussusception is a condition in which part of the intestine becomes trapped inside the intestinal tract on the anal side. The trapped part of the intestine becomes doubled, reducing blood flow and causing congestion. The intestine in that area also becomes blocked. This causes abdominal pain, vomiting, bloody mucus in the stool (similar to strawberry jam), and lethargy. It often occurs in infants around the age of one, and is a condition that requires emergency treatment. It can also be seen in older children.
Intussusception in infants and young children is caused by the swelling of lymphatic tissue in the intestinal tract due to a viral infection, etc. In older children, there may be some kind of disease in the intestinal tract (such as polyps or diverticula).
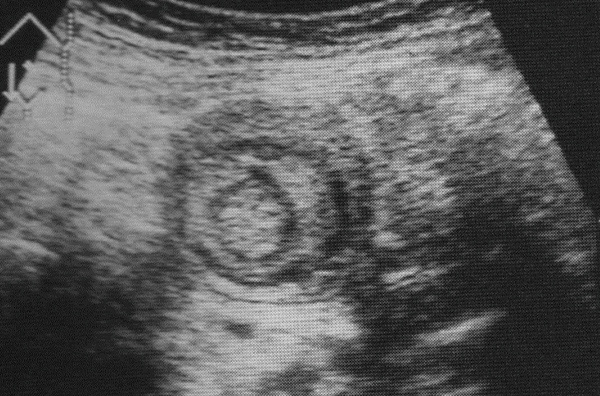
This is an abdominal ultrasound examination. If the trapped, doubled intestine is visible, the diagnosis can be made (this is called the target sign).
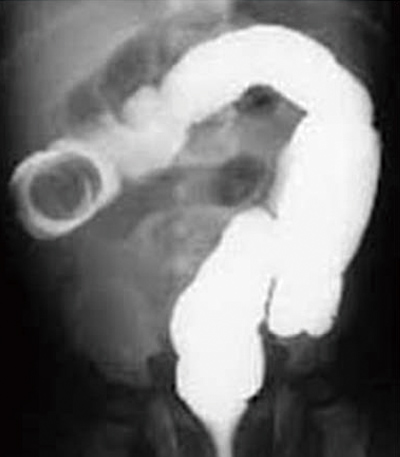
Intussusception should be treated as soon as possible. If it occurs early after onset, it can be treated with a high-pressure enema. Specifically, contrast medium and air are introduced into the anus, and the affected area is repositioned while applying positive pressure. However, if the trapped intestine does not return with this high-pressure enema, surgery is required to correct the trapped intestine. Furthermore, if the intestine remains trapped for a long time and significant damage is caused, the intestine may need to be resected.