
Departments
Gallstones are hard, stone-like structures that form in the gallbladder or bile duct. Gallstones are said to be on the rise among children due to changes in dietary habits and the widespread use of ultrasound examinations.
Gallstones can easily form in children even with temporary dehydration. They are also often caused by diseases that make red blood cells more fragile (heart disease, hereditary spherocytosis, etc.). There may also be hidden bile duct diseases such as congenital biliary dilatation.
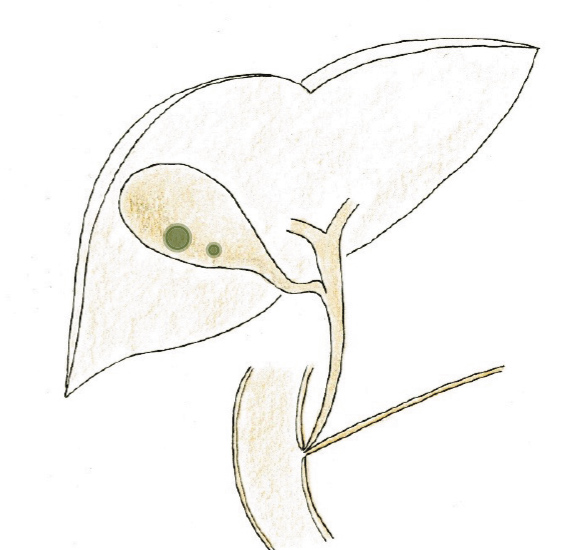

Gallstones are generally found due to abdominal pain, vomiting, jaundice, and fever. However, asymptomatic gallstones can also be discovered by chance during an examination. If a stone falls from the gallbladder into the bile duct, it can impair the flow of bile and pancreatic juice, which can lead to serious complications.
If there are no symptoms or the stones are small, medical treatment such as choleretic drugs may be used. However, depending on the symptoms, surgery to remove the stones along with the gallbladder may be necessary. Even for children, surgery is generally performed using laparoscopic surgery, which leaves a small incision.
Gallbladder and common bile duct stones