
Departments
Appendicitis can sometimes be diagnosed relatively easily, but in children in particular, there are many diseases that cause similar symptoms, and diagnosis requires expertise due to the difficulty of questioning and examination. As appendicitis becomes more difficult to treat and complications increase with the severity, it is important to diagnose and treat it early. In recent years, the usefulness of a scoring system (Table 1) for diagnosing appendicitis at the initial medical stage has been reported, and the "2017 Evidence-Based Guidelines for Abdominal Emergency Care in Children" published by the Japanese Society of Pediatric Emergency Medicine also proposes an algorithm using a scoring system (Figure 1).
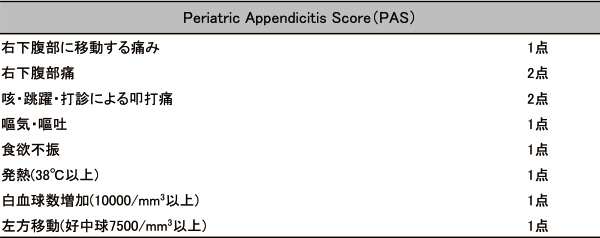
*From the 2017 Evidence-Based Guidelines for Pediatric Abdominal Emergency Care
* Active observation: A procedure in which oral intake is prohibited and fluids are administered intravenously, with physical examinations and repeated tests such as white blood cell count and neutrophil count every 4 to 8 hours.
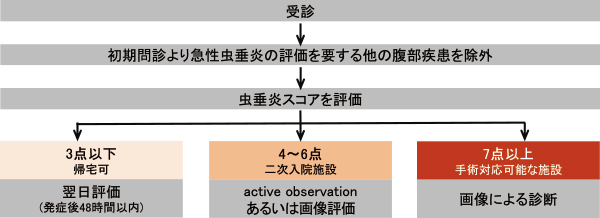
* A total score of 7 or more is considered to be acute appendicitis.
* Samuel M. Pediatric appendicitis score. J Pediatr Surg. 2002;37(6):877-881.