
Departments
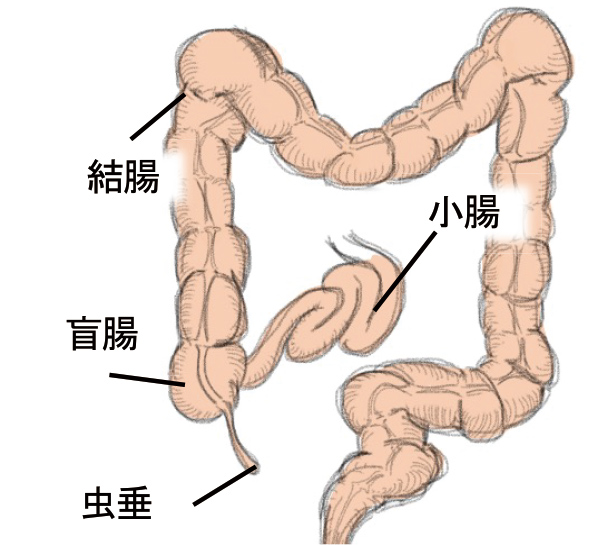
The appendix is a small protrusion that extends from the cecum, the beginning of the large intestine. This area can become inflamed, a condition called appendicitis.
The severity of appendicitis varies greatly depending on the intensity of the inflammation, so it is necessary to comprehensively examine physical findings, ultrasound scans, CT scans, etc., and treatment also varies depending on the stage of the condition.
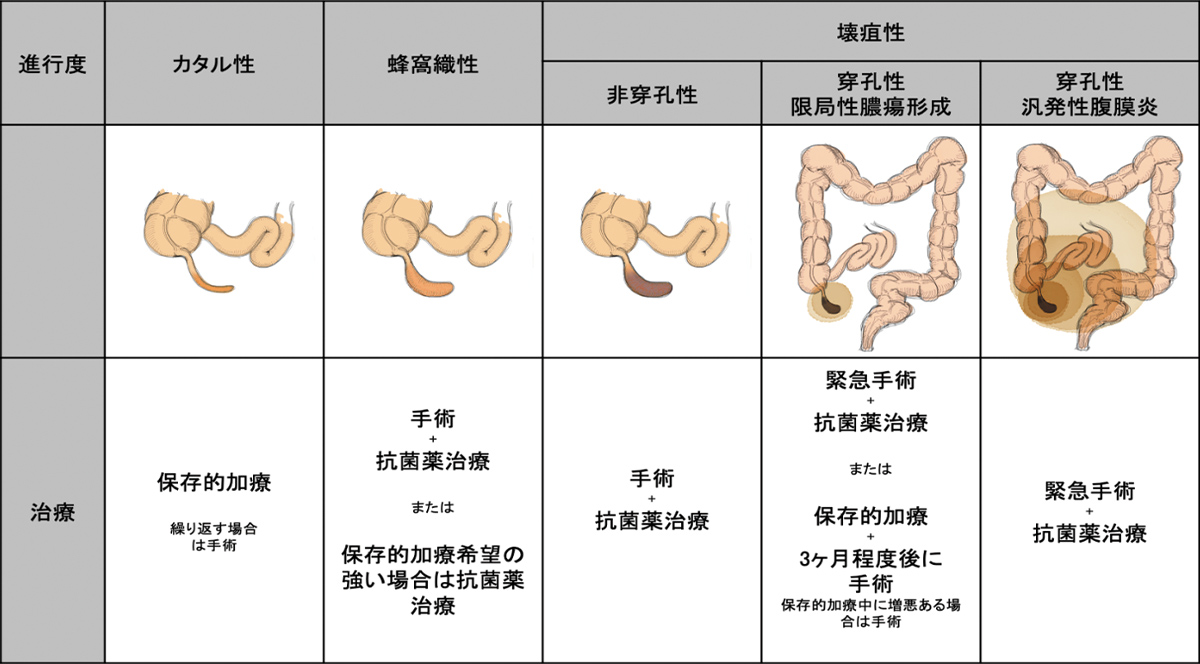
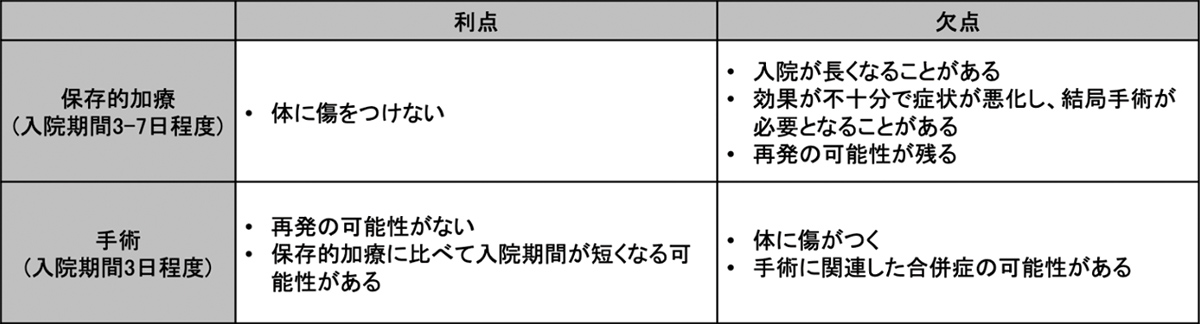
Treatment for appendicitis can be broadly divided into antibiotic treatment and surgical treatment. In many cases, a combination of these treatments is used.
Surgery is generally performed using a laparoscope, which leaves small incisions. The number and location of incisions varies from patient to patient depending on the degree and location of inflammation in the appendix. In rare cases, as the inflammation of appendicitis progresses, adhesions can form between organs within the abdominal cavity, making laparoscopic surgery difficult. In such cases, open surgery may be required.
At our hospital, we take various measures to prevent complications during surgery and perioperative management, but there are cases where complications cannot be avoided, and in such cases additional treatment may be necessary. Since complications increase as the severity of appendicitis increases, it is important to diagnose and treat them promptly.
Bleeding, infection (wound, intraperitoneal cavity), secondary damage (blood vessels, intestines, bladder, ureters, liver, reproductive organs, other intraperitoneal organs)
Postoperative adhesive ileus and umbilical morphological changes