what's new
Until now, when essential tremor, Parkinson's disease tremor, or other Parkinson's disease symptoms were resistant to medical treatment, stereotactic brain surgery, such as deep brain stimulation, has been used to treat these conditions. However, conventional surgery requires drilling the skull and inserting electrodes, and the development of a less invasive treatment has been desired.
Kitano Hospital (Director: Nagahisa Yoshimura, Professor Emeritus, Kyoto University) has collaborated with the Department of Neurosurgery, Chief Director Hiroki Toda, Deputy Director Namiko Nishida, and Chief Director Yoshiyuki Matsumoto of the Department of Neurology, in collaboration with Professor Susumu Miyamoto of the Department of Neurosurgery at the Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, Professor Ryosuke Takahashi of the Department of Neurology, Professor Nobukatsu Sawamoto of the Department of Near-Future Systems and Technology Creation, Department of Human Health Sciences, and the clinical group of Chief Director Makio Takahashi of the Department of Neurology at Osaka Red Cross Hospital to introduce MRI-guided focused ultrasound therapy (FUS), a non-incision surgery that does not involve trepanation or electrode insertion, at Tatsuki Kofukai Kitano Hospital. Kitano Hospital has previously been involved in various neuromodulation treatments, including deep brain stimulation, and this marks the first time that such a neuromodulation center in western Japan has introduced MRgFUS.
The Kitano Hospital/Kyoto University medical group will provide comprehensive treatment for essential tremor and Parkinson's disease by adding FUS to the existing medical treatments, stereotactic brain surgery, and device treatments. At the same time, they plan to develop new treatments, such as iPS cell transplantation, which is currently undergoing clinical trials, and consider optimizing treatment according to the type of disease.
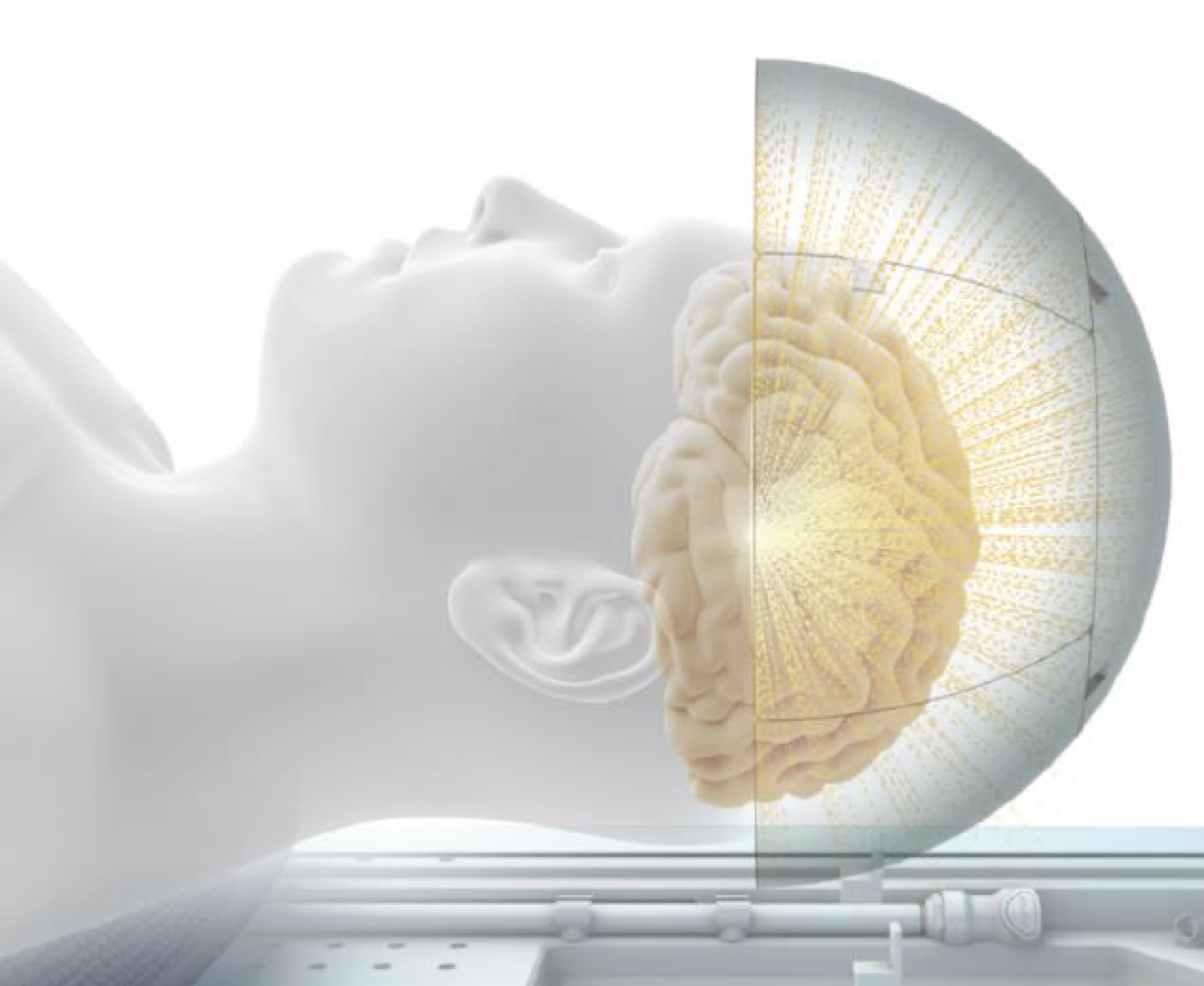
Courtesy of Insightec
The prevalence of essential tremor is approximately 2.5–10% of the population, increasing with age to 41% in those aged 40 years and over and 5–14% in those aged 65 years and over. Tremor manifests during activities such as eating and writing, significantly impacting daily life. The only treatment approved for essential tremor is arotinolol, a beta-sympathetic receptor blocker with side effects such as lowering blood pressure, reducing cardiac function, and worsening asthma. It is therefore not adequately used in elderly patients or those with cardiac or respiratory diseases. Antiepileptic and anti-anxiety drugs are also commonly used, but they induce drowsiness, making medication adherence difficult. Stereotactic surgery has long been used to treat tremors that cannot be controlled with medication. However, because it is a surgical procedure, there are risks of bleeding and infection, making it difficult to recommend surgery to elderly patients.
The overall prevalence of Parkinson's disease is around 0.2%, but it is around 1% for those over 50, and continues to increase with age. The disease also progresses slowly, with symptoms requiring surgery beginning to appear around 10 years after onset. Therefore, by the time surgical treatment is considered, patients are already at an age where surgery is at high risk, making it difficult to actually consider surgery as a treatment option.
FUS, which we will now be introducing at our hospital, is a non-incision surgery that uses ultrasound to create a thermal coagulation nest in the circuit responsible for involuntary movements such as tremors.
Previous stereotactic surgery required scalp incisions, burr holes, and the insertion of electrodes into targets such as the ventral intermediate thalamic nucleus (Vim nucleus) and the internal segment of the globus pallidus. In FUS, a helmet-shaped ultrasound generator called a transducer is attached to the head. The transducer is equipped with 1,024 ultrasound generating elements, which focus ultrasound waves onto a single point on the target, creating a thermal coagulation lesion and achieving the same effects as previously achieved by inserting an electrode.
In patients with essential tremor or severe Parkinson's disease, neural activity in the Vim nucleus is overactive, and thermal coagulation of this area can reduce the overactivity and improve tremors. The tissue temperature is gradually increased to create a thermal coagulation focus in the target area, and treatment is performed while ensuring the therapeutic effect is achieved and there are no side effects. The stiffness and involuntary wriggling movements of the body seen in Parkinson's disease, known as dyskinesia, are caused by overactivity of the internal globus pallidus, and similar thermal coagulation focus is created targeting this area.
As Japan becomes an increasingly super-aged society, the number of patients whose daily lives are limited by essential tremor and Parkinson's disease will continue to increase. Currently, surgical treatment is required for symptoms that cannot be controlled by medical treatment. This ultrasound-based treatment is theoretically free of the risks of intracranial bleeding and infection that were a concern with previous stereotactic brain surgery, eliminating the risk of complications that limited its use in elderly people.
Furthermore, surgical treatment for essential tremor and Parkinson's disease, which are targeted for treatment, should ideally be carried out by a team of multiple medical departments, primarily neurology and neurosurgery, from planning to execution. FUS cannot replace all stereotactic brain surgery that has been performed up to now, and when selecting a treatment, a medical system is needed that compares it with medical treatment, including device-assisted therapy, as well as previous deep brain stimulation therapy and stereotactic ablation.
As a neuromodulation center that can provide various medical and surgical treatment options for involuntary movements, our hospital is the first in western Japan to introduce focused ultrasound therapy. Utilizing our clinical experience to date, we will be advancing a clinical project to verify target visualization in FUS, optimization of treatment options, and long-term treatment outcomes in collaboration with Kitano Hospital and Kyoto University's Department of Neurology and Department of Neurosurgery.
Tremor and Parkinson's Disease Outpatient ClinicPlease check.
For inquiries and interview requests from the media, please contactThis email formPlease contact us at: