Angina pectoris is a condition characterized by chest pain during exertion due to narrowing of the coronary artery lumen caused by coronary arteriosclerosis, which prevents sufficient blood from reaching the heart muscle. Current treatments for angina include drug therapy to slow the heart's activity, balloon therapy to dilate narrowed coronary arteries, and bypass surgery to connect the aorta and coronary arteries. However, each of these treatments has its limitations. For patients still suffering from angina, we offer "heparin accelerated bed therapy." This therapy alleviates and cures angina by developing a natural bypass ("collateral circulation") from another coronary artery to the inadequately supplied myocardium. Specifically, it involves intravenous heparin injection and patient recumbency on a mobile bed. At Kitano Hospital, we have been offering this therapy to patients since January 2007 with the approval of our ethics committee, and its effectiveness has already been demonstrated.
(Miyamoto S, et al: Effect on treadmill exercise capacity, myocardial ischemia, and left ventricular function as a result of repeated whole-body periodic acceleration with heparin pretreatment in patients with angina pectoris and mild left ventricular dysfunction. Am J Cardiol 107:168-74, 2011.)
Since its effectiveness in treating angina pectoris has also been demonstrated, we are now expanding our treatment to include patients with severe heart failure, arteriosclerosis obliterans, and pulmonary hypertension. We look forward to seeing anyone who is interested.
More informationTo herePlease contact us.
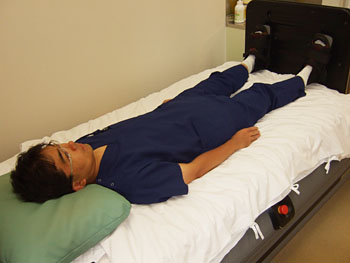
Kitano Hospital played a major role in the clinical development of the accelerated bed, whose main mechanism is to increase nitric oxide in the vascular endothelium, and numerous studies have demonstrated that it improves vascular endothelial function, prevents the progression of arteriosclerosis, and improves coronary artery blood flow reserve. The "accelerated bed therapy for heart failure" being implemented at Kitano Hospital is a groundbreaking treatment that is attracting worldwide attention, and is expected to be a boon to many patients suffering from heart failure.
May 2012
Professor Emeritus, Kyoto University
Honorary Director of Uji Hospital
Masatoshi Fujita